263
information, the foreign currency debtor and creditor positions
and related financial hedging instruments reported by
Prysmian S.p.A. at 31 December 2013 are of limited relevance.
More information can be found in Note 7. Derivatives.
(b) Interest rate risk
The interest rate risk to which the Company is exposed is
mainly due to long-term financial liabilities, carrying both
fixed and variable rates.
Fixed rate debt exposes the Company to a fair value risk. The
Company does not operate any particular hedging policies in
relation to the risk arising from such contracts.
The Group Finance Department monitors the exposure to
interest rate risk and adopts appropriate hedging strategies
to keep the exposure within the limits defined by the Group
Finance, Administration and Control Department, arranging
derivative contracts, if necessary.
The net liabilities considered for sensitivity analysis include
variable rate financial receivables and payables and cash and
cash equivalents whose value is influenced by rate volatility.
The Company calculates the pre-tax impact on the income
statement of changes in interest rates.
The simulations carried out for balances at 31 December
2013 indicate that, with all other variables remaining
equal, an increase of 25 basis points in interest rates would
have decreased financial payables by Euro 146 thousand
(2012: increase of Euro 1,307 thousand), while a 25-point
decrease would have increased financial payables by Euro
146 thousand (2012: decrease of Euro 1,307 thousand). This
simulation exercise is carried out on a regular basis to ensure
that the maximum potential loss is within the limits set by
management.
(c) Price risk
This risk relates to the possibility of fluctuations in the
price of strategic materials, whose purchase price is subject
to market volatility. Following the business reorganisation
discussed in Section A. General information, the Company
is now responsible for centrally managing the purchase of
such materials from third-party suppliers and their resale
to Group operating companies. The Company is exposed to
a residual price risk on those buying positions that have not
been promptly recharged to Group operating companies. More
information about metal derivatives can be found in Note 7.
Derivatives.
(d) Credit risk
The Company does not have significant concentrations of
credit risk insofar as almost all its customers are companies
belonging to the Group. There are also no significant past due
receivables that have not been written down.
(e) Liquidity risk
Prudent management of the liquidity risk arising from the
Company’s normal operations involves the maintenance of
adequate levels of cash and cash equivalents, short-term
securities and funds obtainable from an adequate amount of
committed credit lines. The Company’s Finance Department
prefers flexibility when sourcing funds by using committed
credit lines.
At 31 December 2013, cash and cash equivalents stand at
Euro 4,600 thousand, compared with Euro 681 thousand at 31
December 2012. The Company can potentially draw down the
credit lines granted to the Group in the form of the Revolving
Credit Facility (Euro 400 million) and the EIB Loan (Euro 100
million). More details can be found in the Explanatory Notes
to the Consolidated Financial Statements (Section D. Financial
risk management).
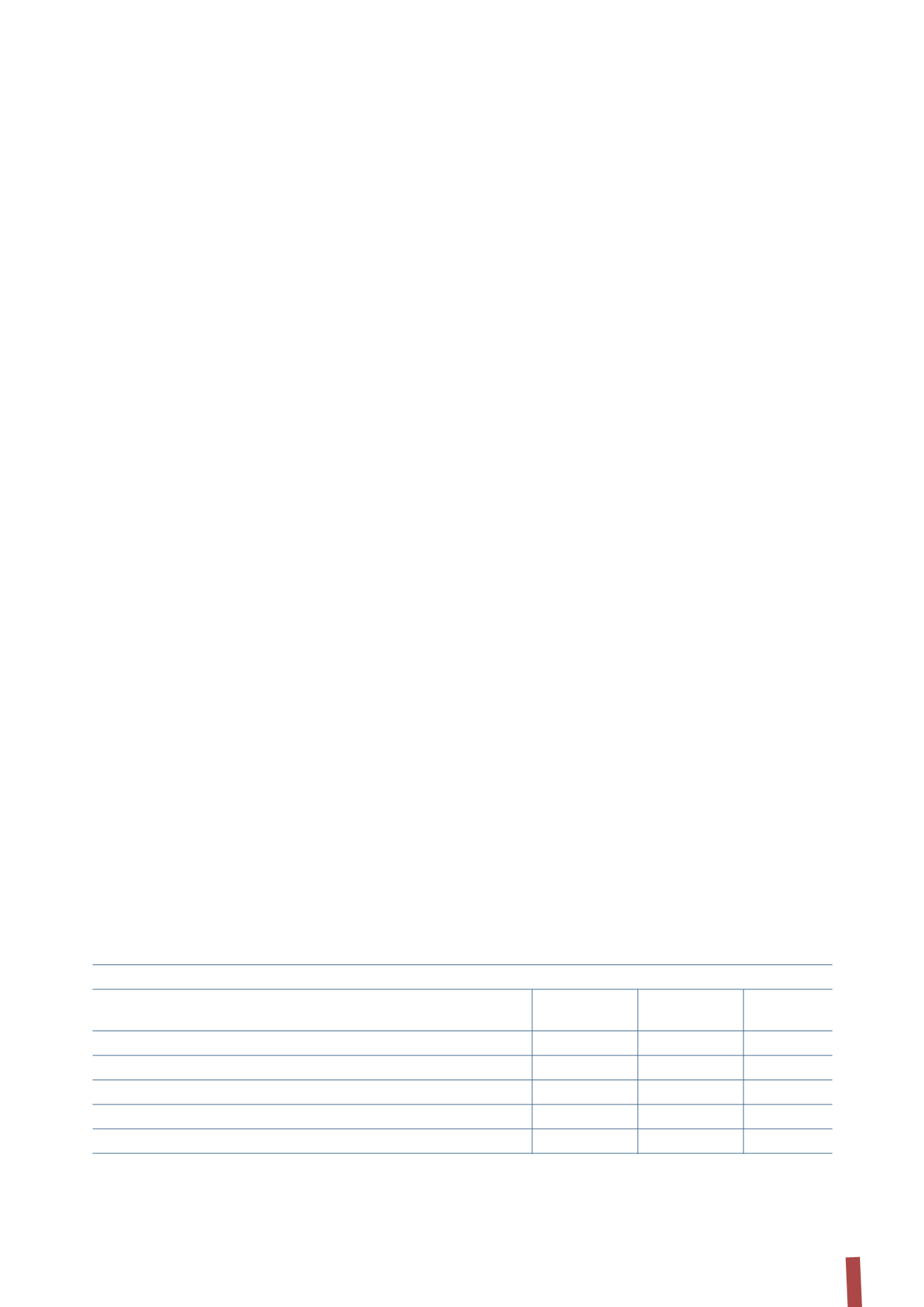
The following table presents an analysis, by due date, of the
payables and liabilities settled on a net basis. The various
due date categories are determined on the basis of the period
between the reporting date and the contractual due date of
the obligations.
(in thousands of Euro)
31 December 2013
Due within
Due between
Due between
Due after
1 year
1-2 years
2-5 years
5 years
Borrowings from banks and other lenders
140,204
418,298
672,715
-
Finance lease obligations
1,428
651
1,952
9,978
Derivatives
88
36
-
-
Trade and other payables
325,051
-
-
-
Total
466,771
418,985
674,667
9,978


