CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL REPORT | EXPLANATORY NOTES
169
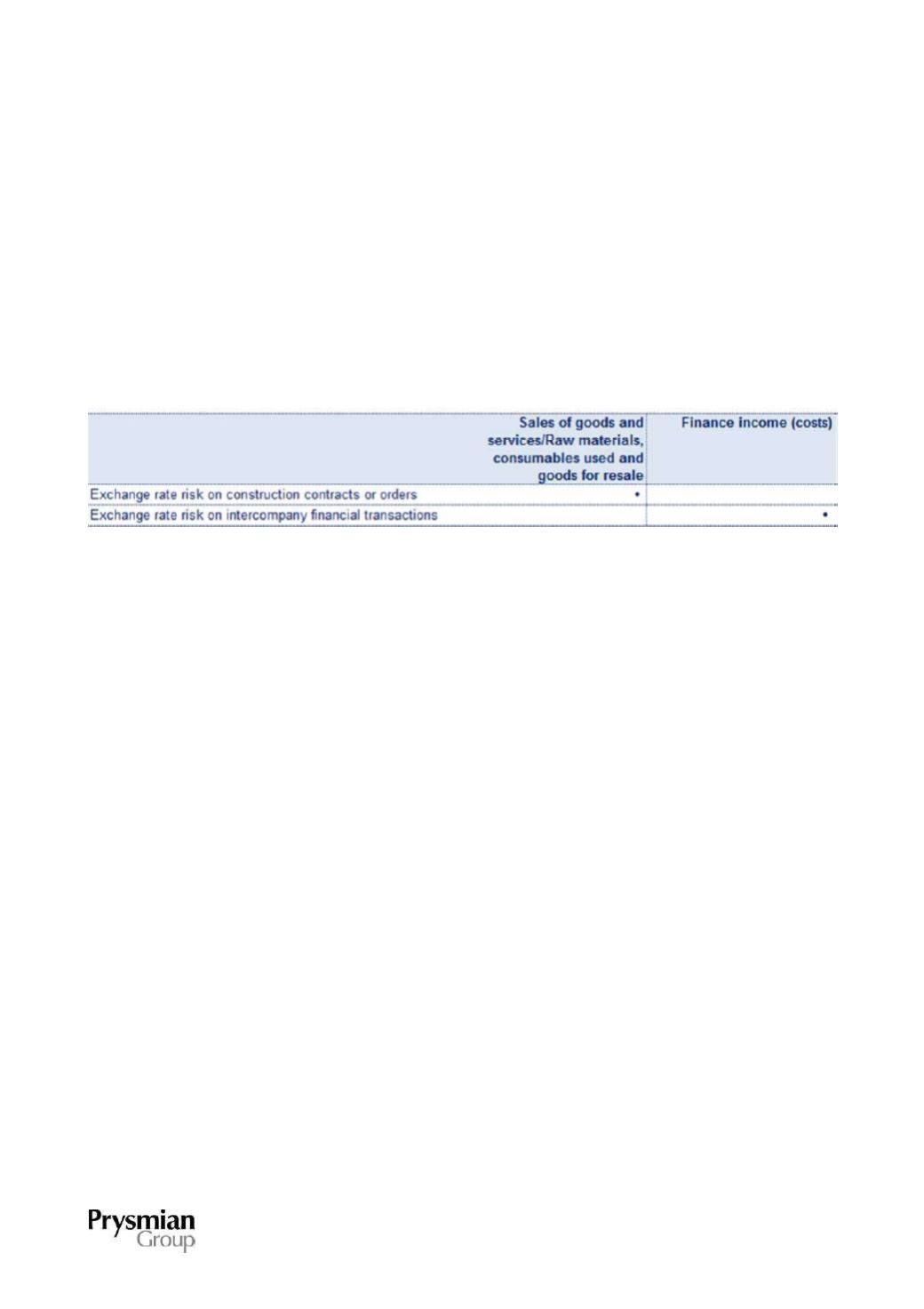
exchange rate risk on intercompany financial transactions:
these hedges aim to reduce volatility
arising from changes in exchange rates on intercompany transactions, when such transactions
create an exposure to exchange rate gains or losses that are not completely eliminated on
consolidation. The economic effects of the hedged item and the related transfer of the reserve to the
income statement occur at the same time as recognising the exchange gains and losses on
intercompany positions in the consolidated financial statements.
When the economic effects of the hedged items occur, the gains and losses from the hedging instruments
are taken to the following lines in the income statement:
B.11 TRADE AND OTHER RECEIVABLES
Trade and other receivables are initially recognised at fair value and subsequently valued on the basis of the
amortised cost method, net of the allowance for doubtful accounts. Impairment of receivables is recognised
when there is objective evidence that the Group will not be able to recover the receivable owed by the
counterparty under the terms of the related contract.
Objective evidence includes events such as:
(a)
significant financial difficulty of the issuer or debtor;
(b)
ongoing legal disputes with the debtor relating to receivables;
(c)
likelihood that the debtor enters bankruptcy or starts other financial reorganisation procedures;
(d)
delays in payments exceeding 30 days from the due date.
The amount of the impairment is measured as the difference between the book value of the asset and the
present value of future cash flows and is recorded in the income statement under "Other expenses".
Receivables that cannot be recovered are derecognised with a matching entry through the allowance for
doubtful accounts.
The Group makes use of without-recourse factoring of trade receivables. These receivables are
derecognised because such transactions transfer substantially all the related risks and rewards of the
receivables to the factor.