89
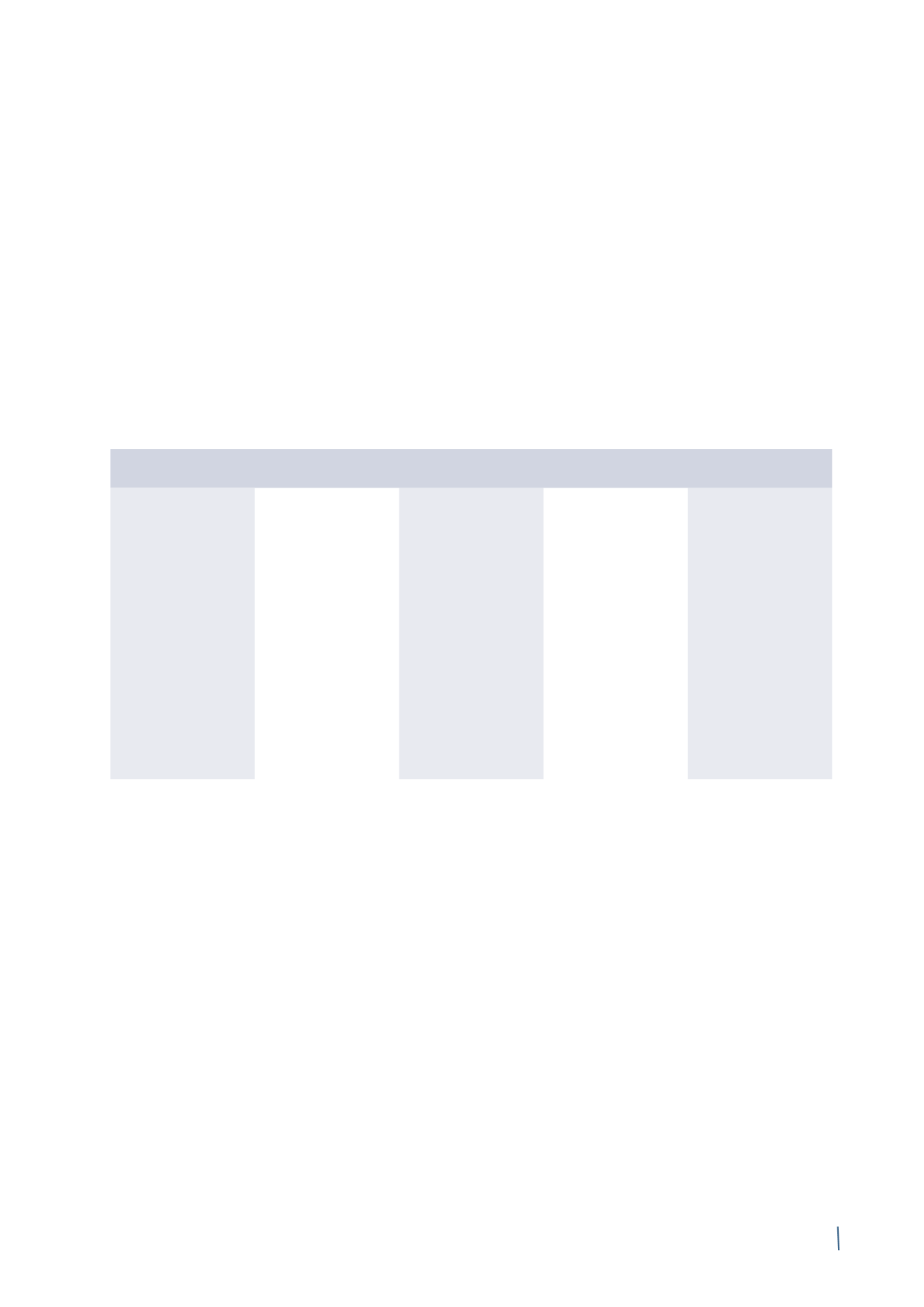
THE PRYSMIAN RISK MODEL
Strategic
Financial
Operational
Legal & Compliance
Planning & Reporting
• Changes in macroeconomic
and competitive
environment and
in demand
• Key customers and
business partners
Emerging market risk
• M&A/JVs and related
integration process
• Commodity price
fluctuation
• Exchange rate fluctuations
• Interest rate fluctuation
• Financial instruments
• Credit risk
• Liquidity / Working capital
• Availability / Cost of capital
• Financial counterparties
• Business interruption /
catastrophic events
• Contract performance /
contractual liability
• Product quality / product
liability
• Environment
• Compliance with laws
and regulations
• Compliance with Code
of Ethics, policy and
procedures
• Budget & strategic
planning
• Tax planning & financial
planning
• Management reporting
• Financial reporting
Members of management involved in the ERM process
are required to use a clearly defined common method to
measure and assess specific risk events in terms of Impact,
Probability of occurrence and adequacy of the existing Level
of Risk Management, meaning:
• economic-financial impact
on expected EBITDA or cash
flow, net of any insurance cover and countermeasures
in place and/or qualitative type of impact on reputation
and/or efficiency and/or business continuity, measured
using a scale that goes from
negligible
(1) to
critical
(4);
• probability
that a particular event may occur within the
specific planning period, measured using a scale that
goes from
remote
(1) to
high
(4);
• level of control
meaning the maturity and efficiency
of existing risk management systems and processes,
measured using to a scale that goes from
adequate
(green) to
inadequate
(red).
The overall assessment must also take into account the
future outlook for risk, or the possibility that in the period
considered the exposure is increasing, constant or decreasing.
The results of measuring exposure to the risks analysed
are then represented on a 4x4 heat map diagram, which, by
combining the variables in question, provides an immediate
overview of the risk events considered most significant.
• Strategic Risks: risks arising from external or internal
factors such as changes in the market environment,
bad and/or improperly implemented corporate decisions
and failure to react to changes in the competitive en-
vironment, which could therefore threaten the Group's
competitive position and achievement of its strategic
objectives;
• Financial Risks: risks associated with the amount of
financial resources available, with the ability to manage
currency and interest rate volatility efficiently;
• Operational Risks: risks arising from the occurrence of
events or situations that, by limiting the effectiveness
and efficiency of key processes, affect the Group's ability
to create value;
• Legal and Compliance Risks: risks related to violations
of national, international and sector-specific legal and
regulatory requirements, to unprofessional conduct
in conflict with company ethical policies, exposing the
Group to possible penalties and undermining its reputa-
tion on the market;
• Planning and Reporting Risks: risks related to the
adverse effects of incomplete, incorrect and/or untimely
information with possible impacts on the Group's
strategic, operational and financial decisions.