Sustainable mobility is no longer a buzzword, it's a necessity driven by the urgent need to combat climate change and reduce our carbon footprint. As the world tries to meet the challenges of decarbonization and environmental conservation, the shift towards electric vehicles (EVs) is becoming a reality.
What you will find in this article
- What do we mean by sustainable mobility?
- The correlation between sustainable mobility and decarbonization;
- The rise of electric vehicles;
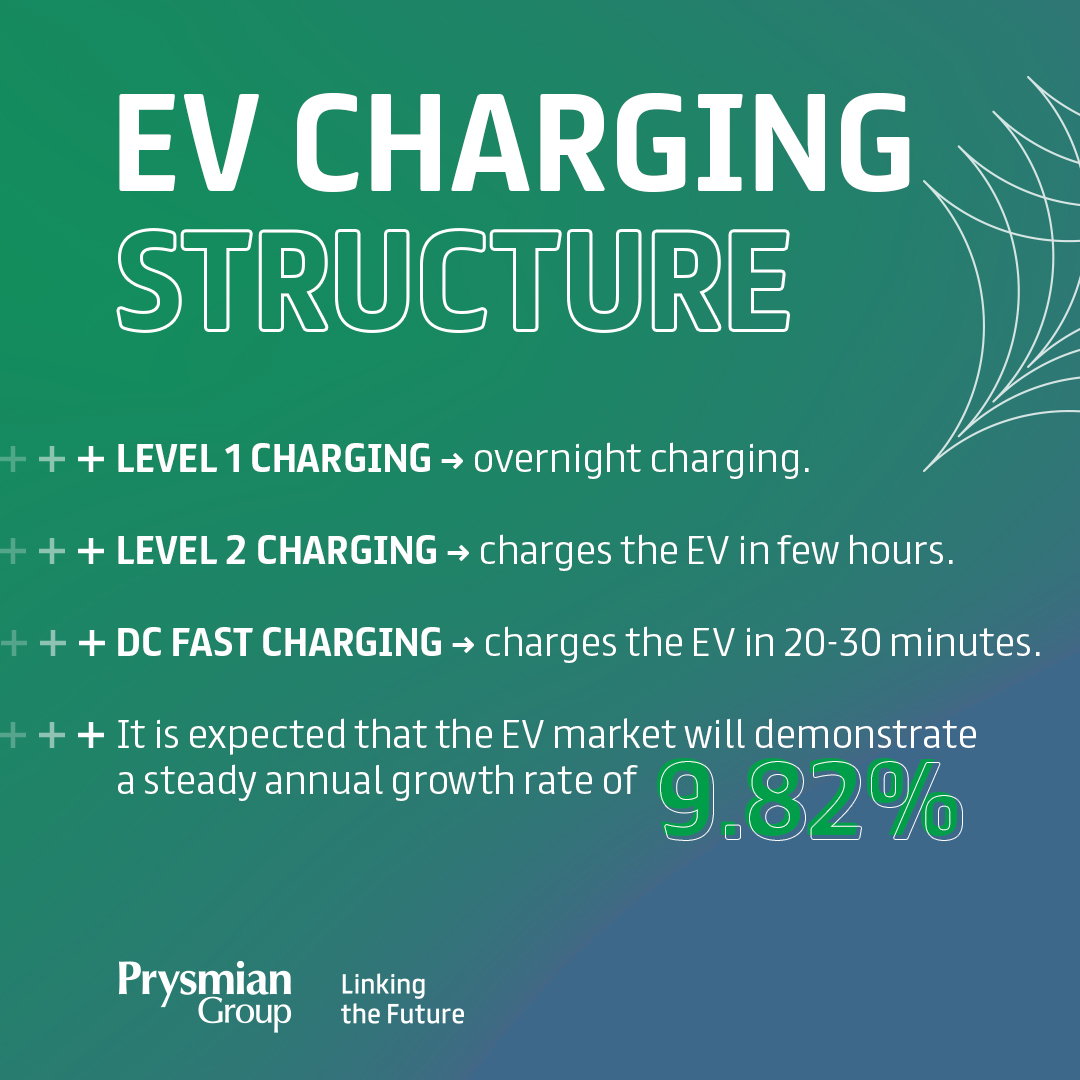
- Types of charging infrastructure
- What is Formula E and what are its perks