Materiality Matrix 2024
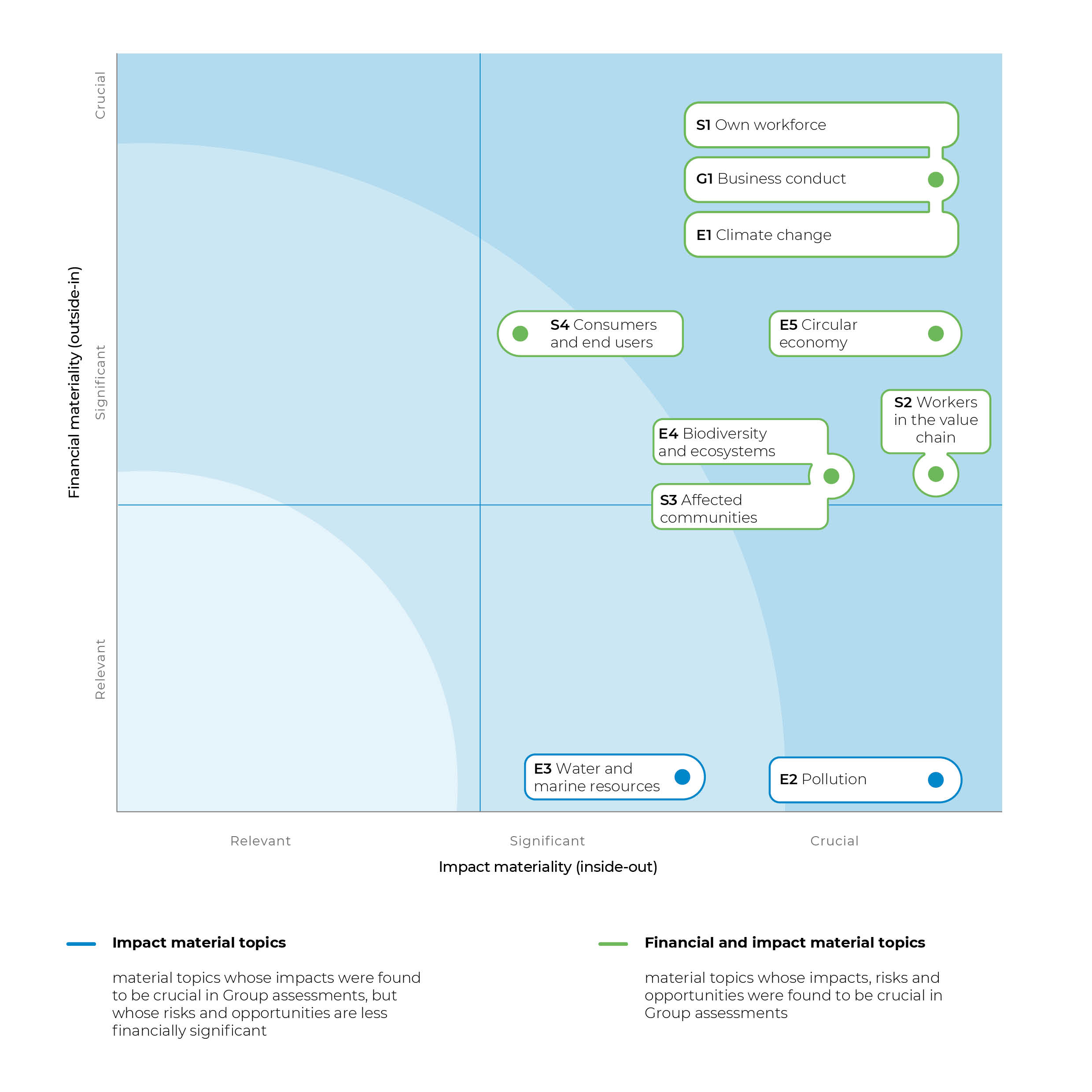

Prysmian's dual materiality analysis is represented graphically through a matrix that highlights the correlation between impact materiality and financial materiality. For each theme defined by ESRS, two aspects are considered: the impact the company has on the outside world, positioned on the x-axis, and the risk/opportunity that may affect the company's financial performance, positioned on the y-axis.
The matrix is structured to evaluate each theme according to two main dimensions:
1. Impact materiality: represents the magnitude of the effect that the company's activity generates or may generate on the environment, people and community, considering factors such as the geographic distribution of the impact, its irreversibility and the likelihood of its occurrence.
2. Financial materiality: it measures the economic effect the issue in question may have on the company, both in terms of risks (such as unforeseen costs, penalties, reputational damage) and opportunities (e.g., economic benefits from adopting sustainable solutions or competitive advantages).
ESG issues are placed in the matrix based on the internal analysis conducted during the year by the company and shared with external stakeholders, taking into consideration the highest value associated with the impacts, risks and opportunities related to each ESRS issue. In this way, the matrix provides a clear representation of the areas with the highest overall score, considering the scale of impact, risk and opportunity, as well as the irreversibility and probability of events.
All the issues mapped in the matrix, as well as the associated impacts, risks and opportunities, are considered material.
This visualization makes it easy to identify priorities for the company, directing efforts toward those issues that present the most significant combination of impact and financial materiality, and thus require immediate strategic attention:

As required by the ESRS, the identified impacts were analyzed and evaluated as follows:
Prysmian examined the transition risks associated with increasing regulatory pressure and the transition to a low-carbon economy. The introduction of stricter climate change and sustainability regulations involved a careful assessment of the immediate financial effects, such as the technological adaptation needed to meet environmental standards.
In parallel, the financial effects from ESG opportunities were explored. Prysmian identified areas where the adoption of more sustainable and innovative solutions could generate a positive return. Expansion in these areas has had a direct impact on revenues, with increased sales related to innovative and "green" segments (such as, for example, the Pry-Cam range and P-Laser cable) and increased attractiveness to environmentally sensitive customers and investors.
For impact materiality, the threshold identified was 2.5 (disclosure level); impacts with a final value below 2.5 were not considered material. In contrast, impacts whose final assessment was between 2.5 (disclosure level) and 4 (crucial level) were considered material.
For financial materiality, the threshold chosen was 2 (disclosure level) in order to provide a more complete representation of risks and opportunities for Prysmian. As a result, the risks and opportunities with a final value below 2 were not considered material.
The dual materiality assessment was studied in-depth through a number of key resources, which provided a comprehensive view of the Group's operations and the business relationships that characterize its supply chain:

The impacts, risks and opportunities were identified through the involvement of the functions most exposed to relationships within the Group's value chain and those that operate in connection with elements related to the IRO themselves.